In the realm of psychology, few theories have had as significant an impact as the Maslow hierarchy of needs. The Maslow hierarchy of needs theory, developed by psychologist Abraham Maslow in the mid-20th century, remains influential in understanding human motivation and behavior. This article will delve deep into the Maslow hierarchy of needs, exploring its key psychological concepts, and illustrate how this theory influences human actions and drives. To bring this theory to life, we will also provide real-world Maslow hierarchy of needs examples. So, whether you are a student of psychology, a professional in the field, or simply an individual intrigued by human behavior, this comprehensive guide on the Maslow hierarchy of needs explained will be an enlightening read.
1. “Understanding the Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Theory: A Deep Dive”
The Maslow hierarchy of needs theory, developed by psychologist Abraham Maslow in the 1940s, is a critical psychological concept that has significantly influenced our understanding of human motivation and behavior. By delving into the Maslow hierarchy of needs explained, we can gain a deeper appreciation of the factors that drive our actions every day.
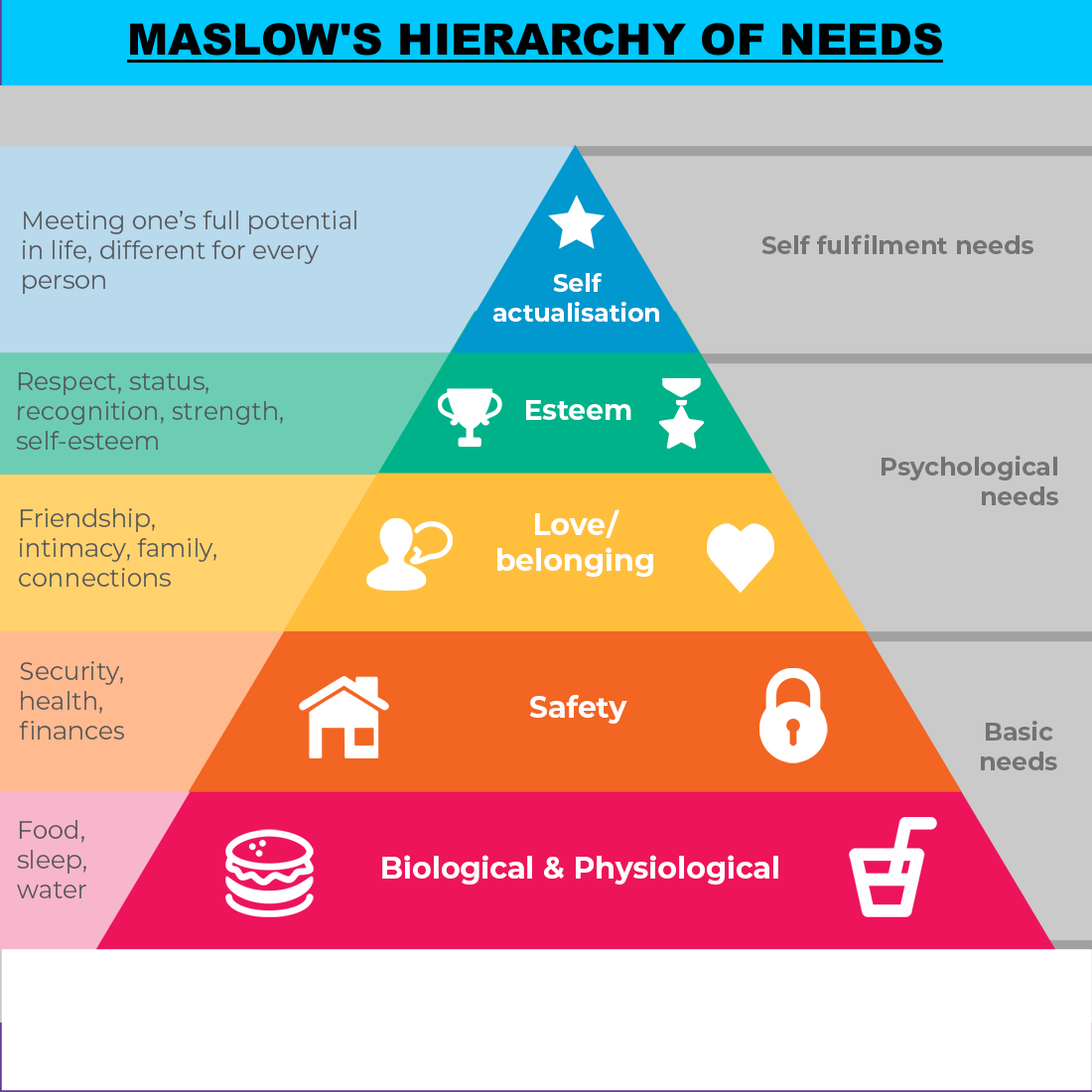
At its essence, the Maslow hierarchy of needs theory proposes that people are motivated to achieve distinct types of needs. These needs are often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. Starting from the base, the levels include physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization needs.
Physiological needs, the first and most basic level, pertain to our fundamental survival requirements, such as food, water, and sleep. Once these needs are met, we can then focus on safety needs, which involve security, stability, and freedom from fear. This is followed by love/belonging needs, which correspond to our desires for interpersonal relationships, affection, and a sense of belonging.
The fourth level includes esteem needs, which involve the desire for respect, self-esteem, and recognition. Finally, at the peak of the pyramid, we have self-actualization needs, which pertain to the realization of one’s potential and the quest for personal growth and self-fulfillment.
To provide some Maslow hierarchy of needs examples, consider an individual who has just lost their job. Their primary focus would likely be on physiological needs (securing food and shelter) and safety needs (finding a new job to ensure financial security). Only when these needs are adequately met can they concentrate on higher-level needs such as love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization.
The Maslow hierarchy of needs theory suggests that unmet needs at lower levels can inhibit individuals from pursuing higher-level needs. This concept provides a comprehensive framework to understand human motivation, explaining why people behave in certain ways based on their unfulfilled needs.
By exploring the Maslow hierarchy of needs, we can better understand the underlying motivations behind human behavior, offering valuable insights into how individuals can achieve satisfaction and fulfillment in their lives.
2. “Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Explained: Key Psychological Concepts”
The Maslow hierarchy of needs is a significant psychological theory that outlines the fundamental needs that drive human behavior. This key model in understanding human motivation was proposed by Abraham Maslow in 1943. The Maslow hierarchy of needs explained the different levels of needs that individuals aim to meet, starting from basic survival needs to more complex psychological needs.
The first level of the Maslow hierarchy of needs is physiological needs, which include basic requirements for human survival such as food, water, sleep, and warmth. These are the most potent needs because if a person is deprived of all needs, the physiological ones must be satisfied first.
The second level in Maslow hierarchy of needs theory is safety needs. Once the physiological needs are met, the individual’s attention shifts to seeking safety and security, including health, employment, and family security. Maslow also included financial security and law and order in this category.
The third level is belongingness and love needs. After physiological and safety needs are fulfilled, the third layer of human needs emerges, that is, the interpersonal and involves feelings of belongingness. This level is about relationships, love, and affection.
The fourth level is esteem needs, which Maslow classified into two categories. The first is self-esteem which results from competency or mastery of a task. Secondly, there’s the attention and recognition that comes from others.
Finally, at the top of the Maslow hierarchy of needs is self-actualization. Maslow described this as the desire to accomplish everything that one can, to become the most that one can be.
To illustrate these concepts, let’s consider some Maslow hierarchy of needs examples. If a person is hungry and homeless (physiological needs), they will not be interested in attending a social event (belongingness and love needs). Only when the basic needs are met can an individual focus on higher-level needs.
These key psychological concepts in the Maslow hierarchy of needs theory play integral roles in influencing human motivation and behavior. The theory suggests that human behavior is motivated by the desire to meet these needs. The inability to satisfy any level of need in the hierarchy can lead to feelings of dissatisfaction and unrest, acting as a driving force for individuals to fulfill these needs.
Understanding the Maslow hierarchy of needs can provide valuable insights into why people behave the way they do and how their needs drive their actions and desires. It offers a framework for psychologists, managers, and educators to better understand motivation and address people’s needs effectively.
3. “How Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Influences Human Motivation and Behavior”
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory is a fundamental psychological framework that has greatly influenced our understanding of human motivation and behavior. At its core, it suggests that our actions and motivations are driven by the need to fulfill specific levels of needs.
The Maslow hierarchy of needs is typically represented as a five-tier pyramid. At the bottom are the most basic physiological needs, such as food, water, and sleep. Once these are met, individuals move up to the second level, which involves safety needs like security, stability, and protection from harm. The third level caters to our social needs for love, affection, and a sense of belonging. The fourth level addresses esteem needs, encompassing respect, self-esteem, and personal worth. At the top of the pyramid are self-actualization needs, which involve realizing and fulfilling personal potential.
Understanding the Maslow hierarchy of needs explained can help us understand why people behave the way they do. For instance, if an individual’s basic physiological needs are not met, they will be primarily motivated to secure those needs above all else. This can explain behaviors such as working long hours at a low-paying job just to afford food and shelter.
Maslow hierarchy of needs examples can be seen in everyday life. For instance, a student might be motivated to study hard and earn good grades (esteem needs) but if they are constantly hungry and lack a safe place to sleep (physiological and safety needs), their focus will inevitably shift to meeting those basic needs first.
Similarly, the theory suggests that people who have satisfied their lower-level needs will be motivated to fulfill higher-level needs. So, someone who has a stable job and a loving family (physiological, safety, and social needs met) might strive to gain recognition in their field (esteem needs) or pursue personal growth and self-improvement (self-actualization needs).
In conclusion, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory provides a dynamic perspective on human motivation and behavior. It suggests that our behaviors are not random or arbitrary, but rather driven by the innate desire to satisfy a series of hierarchical needs. This understanding can be useful in a range of fields, from psychology and counseling to marketing and human resources, providing a framework for understanding and predicting human behavior.
4. “Real-Life Applications: Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Examples”
The Maslow hierarchy of needs theory is a psychological framework that has been widely adopted in various real-world applications. The theory underscores the idea that certain human needs take precedence over others, and we are motivated to fulfill these needs in a particular order, from physiological needs to self-actualization. Here are some real-life applications of the Maslow hierarchy of needs examples that underscore the influence of these concepts on human motivation and behavior.
In the field of education, the Maslow hierarchy of needs theory is often employed to ensure that students are in an optimal state for learning. For instance, schools provide free or discounted meals to ensure that students’ physiological needs are met, which is the first level of Maslow’s hierarchy. Schools also focus on creating a safe and secure environment, addressing the second level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, safety needs. Only when these basic needs are met can students effectively pursue higher order needs such as esteem and self-actualization, which can be fostered through academic achievements and extracurricular activities.
In the business world, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs explained that employees are also driven by this tiered system of needs. Companies often provide sufficient salaries to meet their employees’ basic physiological needs and provide a safe working environment to cater to their safety needs. They further foster a sense of belonging by encouraging teamwork and promoting a positive company culture. Recognition and opportunities for advancement cater to the esteem needs. Finally, to facilitate self-actualization, companies might offer opportunities for employees to take on challenging projects that allow them to utilize and expand their skills.
In the healthcare industry, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is also applied. Medical professionals ensure that patients’ physiological needs are prioritized, such as the need for food, water, and medication. The need for safety and security is addressed by providing a secure environment and ensuring patients understand their medical conditions and treatment plans. Emotional support from medical staff and family caters to the need for love and belonging. The esteem need can be supported by acknowledging patients’ strength and resilience, and the need for self-actualization can be addressed by helping patients regain autonomy and control over their lives.
These Maslow hierarchy of needs examples showcase the practical applications of this theory in various aspects of daily life. Understanding and applying this theory can significantly enhance our understanding of human motivation and behavior, leading to more effective strategies in education, business, healthcare, and other fields.
In conclusion, the Maslow hierarchy of needs theory provides a comprehensive framework that helps us understand the fundamental psychological drivers of human behavior and motivation. Delving deep into Maslow hierarchy of needs explained, we see how basic needs like physiological and safety needs form the foundation, while esteem and self-actualization needs shape our highest pursuits. The theory’s real-life applications reinforce its relevance today, with countless Maslow hierarchy of needs examples found in everyday scenarios. As we navigate our personal and professional lives, the principles of the Maslow hierarchy of needs theory serve as a guide, shedding light on what truly motivates us and influences our behavior. Ultimately, Maslow’s theory underscores the inherent human quest for growth, fulfillment, and understanding, reminding us of our potential to transcend basic needs and strive for self-actualization.